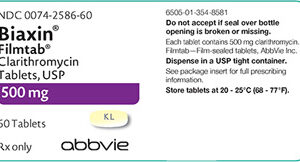
About Biaxin
Biaxin, which is the brand name for clarithromycin, belongs to the group of medications known as macrolide antibiotics. It is designed to combat various bacterial infections by inhibiting the growth of bacteria or killing them outright. Clarithromycin operates by binding to the ribosomal subunits of bacteria, suppressing protein synthesis, which is critical for bacterial survival and replication.
Indications and Usage
Biaxin is indicated for the treatment of numerous types of bacterial infections affecting the skin and respiratory system. It is also used in combination with other medications to eliminate Helicobacter pylori, the bacterium associated with peptic ulcers. Additionally, off-label uses may include treatment of certain types of mycobacterial infections.
Dosage and Administration
Dosage of Biaxin varies depending on the infection being treated, the patient’s age, weight, kidney function, and other medical conditions. It is commonly taken orally with or without food. For adults, doses typically range from 250 mg to 500 mg every 12 hours. For children, the dose is calculated based on body weight. Biaxin XL, an extended-release form of the medication, is taken once daily. It is crucial to complete the full course of treatment even if symptoms improve to prevent the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Contraindications and Warnings
Biaxin is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to clarithromycin, erythromycin, or any other macrolide antibiotic. Cautious use is advised in patients with liver or renal impairment. Warnings include the potential for severe allergic reactions, Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea, and heart problems due to QT prolongation. It should not be used concurrently with certain medications that can interact with Biaxin.
Drug Interactions
Clarithromycin is known to interact with a variety of medications. These interactions may increase the risk of side effects or reduce the effectiveness of either drug. For instance, it should not be taken with cholesterol-lowering drugs known as statins, certain heart medications, or other antibiotics, without a healthcare provider’s approval. Carefully monitoring by a physician is necessary when taking Biaxin in conjunction with other drugs.
Precautions and Special Considerations
Special considerations need to be given when prescribing Biaxin to individuals with pre-existing conditions such as liver or kidney disease. Additionally, those with certain heart conditions should use Biaxin cautiously, as it may exacerbate symptoms. Regular monitoring, including laboratory tests, may be necessary for some patients. Patients should be advised to report any significant changes in symptoms or new symptoms that arise during treatment.
Adverse Reactions
Common adverse reactions to Biaxin may include stomach upset, nausea, vomiting, and changes in taste. In some cases, more severe reactions can occur, such as liver dysfunction, severe allergic reactions, or Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea. If side effects are severe or persist, patients should contact their healthcare provider.
Overdosage and Management
In the event of an overdose, symptomatic and supportive measures should be initiated. As there is no specific antidote for clarithromycin, treatment should be focused on managing the symptoms and providing supportive care. Gastric lavage and monitoring of vital signs are recommended. Medical assistance should be sought immediately if an overdose is suspected.
Clinical Pharmacology
Biaxin undergoes metabolism in the liver and is excreted mainly in the bile and urine. The half-life of the drug can vary but typically ranges between 3 to 7 hours. Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics may be altered in patients with hepatic impairment. Biaxin’s action as a strong inhibitor of the cytochrome P450 system should also be taken into consideration when prescribing concurrent medications.
Storage and Handling
Biaxin should be stored at room temperature away from light and moisture. Tablets and oral suspension should be kept in their original packaging until ready to use. It is essential to keep all medications out of reach of children and pets and to dispose of any expired or unused medication responsibly.
Patient Counseling Information
Patients prescribed Biaxin should be counseled about the importance of adhering to the full course of therapy, potential side effects, and the need to avoid specific drugs that may interact with clarithromycin. It is also vital to inform patients about the signs of an allergic reaction and instruct them to seek immediate medical attention if they experience such symptoms.
Use in Specific Populations
Biaxin should be used with caution in pregnant and breastfeeding women, only when absolutely necessary. Pediatric use should be guided by the child’s weight and the severity of the infection. For geriatric patients, dosage adjustments may be required based on kidney function and overall health status. This medication should also be cautiously administered in patients with pre-existing health conditions.
References
A comprehensive list of references regarding Biaxin’s pharmacology, efficacy, safety profile, and guidelines can be provided by healthcare institutions, pharmaceutical compendia, and peer-reviewed medical publications. For up-to-date information, medical professionals should refer to the latest clinical studies and recommendations for the use of clarithromycin in various patient populations.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.